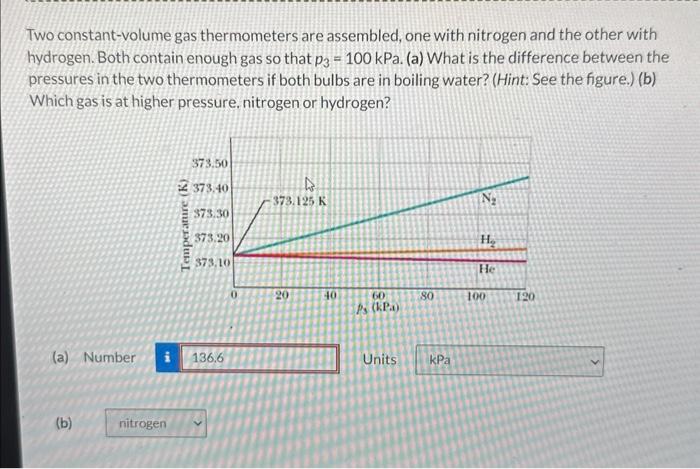
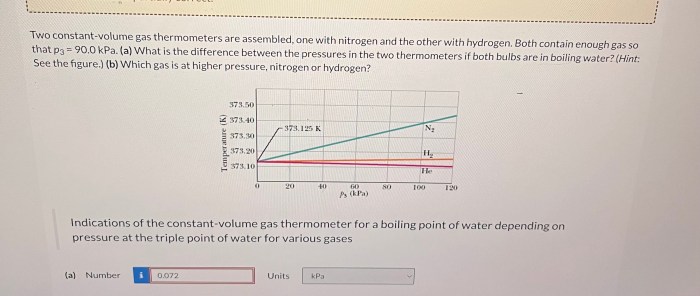
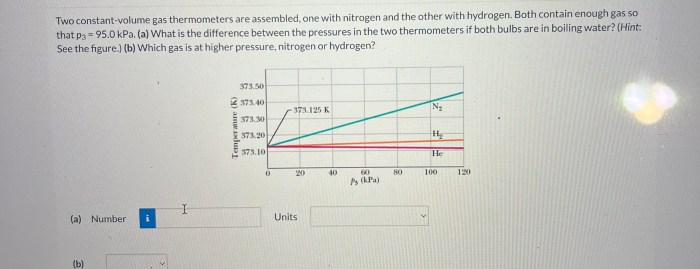
Two constant-volume gas thermometer are assembled – With two constant-volume gas thermometers assembled, we embark on a scientific adventure to explore the intricacies of gas behavior and temperature measurement. This guide delves into the construction, operation, and applications of these remarkable instruments, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance in various fields.
Two constant-volume gas thermometers are meticulously assembled to precisely measure temperature by exploiting the fundamental properties of gases. Their unique design and operation offer distinct advantages, making them indispensable tools in scientific research and industrial processes.
1. Overview of the Two Constant-Volume Gas Thermometers

Constant-volume gas thermometers are precise instruments used to measure temperature by observing the changes in pressure of a gas at a constant volume. They play a crucial role in defining the International Temperature Scale and serve as primary standards for temperature calibration.
Construction and Operation
- Two constant-volume gas thermometers are constructed with identical glass bulbs connected to manometers filled with mercury.
- One thermometer is kept at a reference temperature, typically the triple point of water (0.01 °C), while the other is exposed to the unknown temperature.
- As the temperature of the unknown gas changes, its pressure also changes, which is measured by the manometer.
- The ratio of the pressures in the two thermometers is directly proportional to the ratio of their absolute temperatures.
Advantages and Limitations
Constant-volume gas thermometers offer high accuracy and precision over a wide temperature range.
- Advantages:Precise, accurate, stable, wide temperature range.
- Limitations:Bulky, fragile, requires skilled operators, calibration is complex.
2. Assembling the Two Constant-Volume Gas Thermometers
Materials and Equipment
- Two glass bulbs
- Two mercury manometers
- Connecting tubes
- Vacuum pump
- Gas supply
- Temperature-controlled bath
Assembly Steps
- Clean and dry all components.
- Connect the glass bulbs to the manometers and connecting tubes.
- Evacuate the system using the vacuum pump.
- Fill one bulb with a known gas at a constant volume.
- Immerse the reference bulb in the temperature-controlled bath.
- Calibrate the manometers using the triple point of water.
Importance of Accuracy and Precision
Accurate and precise assembly is crucial for reliable temperature measurements. Any leaks or impurities in the system can affect the accuracy of the readings.
3. Experimental Setup and Procedure
Experimental Setup
The two thermometers are placed in a temperature-controlled environment, with one bulb exposed to the unknown temperature and the other kept at the reference temperature.
Measurement Techniques, Two constant-volume gas thermometer are assembled
- Record the pressure in both manometers.
- Calculate the ratio of the pressures.
- Use the ratio to determine the absolute temperature of the unknown gas.
Potential Sources of Error
- Leaks in the system
- Impurities in the gas
- Temperature fluctuations
- Human error in reading the manometers
Minimizing Error
- Use high-quality components and assemble the system carefully.
- Calibrate the thermometers regularly.
- Control the temperature environment precisely.
- Take multiple readings and average the results.
4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data Analysis
The ratio of the pressures in the two thermometers is used to calculate the absolute temperature of the unknown gas using the following formula:
T unknown= T reference× (P unknown/ P reference)
Interpretation of Results
The calculated absolute temperature provides an accurate measurement of the unknown temperature. This information can be used for various scientific and industrial applications.
5. Applications and Implications
Applications
- Calibration of other thermometers
- Temperature measurements in research laboratories
- Industrial processes requiring precise temperature control
Implications
Constant-volume gas thermometers play a crucial role in defining the International Temperature Scale and advancing our understanding of the properties of gases. They have enabled accurate temperature measurements across various fields, contributing to scientific advancements and technological innovations.
FAQ: Two Constant-volume Gas Thermometer Are Assembled
What are the advantages of using constant-volume gas thermometers?
Constant-volume gas thermometers offer several advantages, including high accuracy and precision, wide temperature range, and independence from the shape and size of the bulb.
How do constant-volume gas thermometers measure temperature?
Constant-volume gas thermometers measure temperature by measuring the pressure of a gas at constant volume. The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature.
What are some applications of constant-volume gas thermometers?
Constant-volume gas thermometers are used in a variety of applications, including scientific research, industrial processes, and temperature calibration.