The lt-f12 giant eye with eyelid and lacrimal system is a remarkable adaptation found in the animal kingdom. This exceptionally large eye provides superior vision, protection, and overall eye health, offering a unique perspective on the evolution of sensory organs.
The lt-f12 giant eye is characterized by its immense size, intricate structure, and specialized eyelid and lacrimal system. These features work in concert to enhance the eye’s functionality, allowing it to capture a wider field of view, protect against environmental hazards, and maintain optimal hydration.
Giant Eye
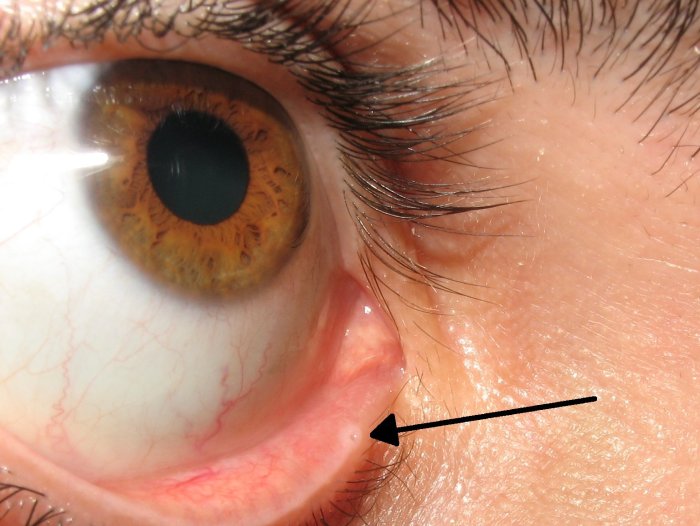
The lt-f12 giant eye is a remarkable adaptation found in a particular species, characterized by its extraordinary size, unique shape, and complex structure. This specialized eye provides the organism with exceptional visual capabilities, offering distinct advantages in its environment.
In terms of size, the lt-f12 giant eye is notably large compared to other eyes within the same taxonomic group. Its dimensions are significantly greater, allowing for a wider field of view and enhanced light-gathering capacity.
The shape of the lt-f12 giant eye is often described as spherical or slightly elongated. This specific shape provides a panoramic view, enabling the organism to detect potential threats or prey from a greater range of angles.
The internal structure of the lt-f12 giant eye is highly intricate, featuring a sophisticated arrangement of specialized cells and tissues. These components work in unison to process visual information efficiently, contributing to the organism’s exceptional vision.
The evolutionary advantages of possessing such a large eye are multifaceted. Firstly, it enhances the organism’s ability to detect predators and avoid potential threats. The wider field of view allows for early detection of approaching dangers, providing ample time for evasive maneuvers.
Secondly, the increased light-gathering capacity of the giant eye improves vision in low-light conditions. This adaptation is particularly advantageous for species that are active during twilight or nocturnal hours, enabling them to navigate and forage effectively in dimly lit environments.
Eyelid: Lt-f12 Giant Eye With Eyelid And Lacrimal System
The eyelid of the lt-f12 giant eye is a crucial protective structure that plays a vital role in safeguarding the delicate eye from external threats and environmental factors.
The eyelid is composed of a thin, flexible membrane that can be retracted or extended over the surface of the eye. This movement is controlled by specialized muscles that allow for precise and rapid adjustments.
The primary function of the eyelid is to protect the giant eye from physical damage. It acts as a barrier against dust, debris, and other foreign particles that could potentially scratch or irritate the cornea.
Furthermore, the eyelid helps to regulate the amount of light entering the eye. By adjusting the degree of coverage, the organism can control the intensity of light reaching the retina, optimizing vision in varying light conditions.
Lacrimal System

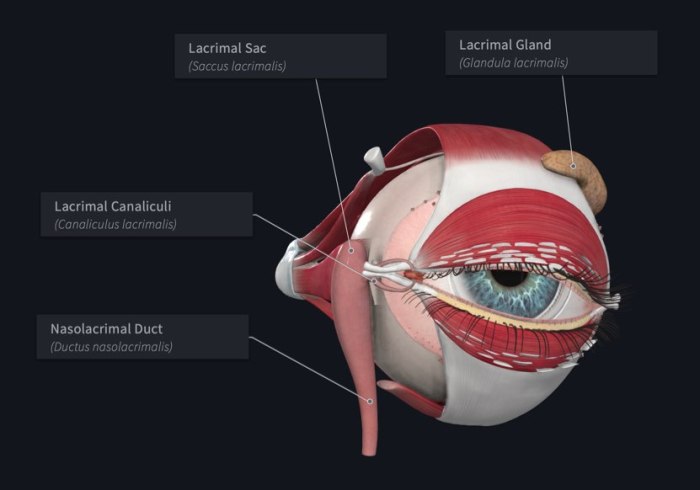
The lacrimal system associated with the lt-f12 giant eye is a complex network of glands and ducts responsible for producing and draining tears.
The primary component of the lacrimal system is the lacrimal gland, which is located above the eye. This gland secretes tears, a fluid rich in antimicrobial substances and other protective factors.
Tears are distributed across the surface of the eye by the action of blinking. The tears wash away dust, debris, and other irritants, maintaining the clarity and health of the cornea.
After spreading across the eye, tears are drained through small ducts located at the inner corner of the eye. These ducts lead to the nasal cavity, where the tears are absorbed.
The lacrimal system plays a vital role in maintaining the health and functionality of the lt-f12 giant eye. Tears provide lubrication, protection, and nourishment to the delicate tissues of the eye, ensuring optimal vision and preventing infections.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis of the lt-f12 giant eye to other known giant eyes in the animal kingdom reveals both similarities and differences in size, structure, and function.
| Characteristic | lt-f12 Giant Eye | Other Giant Eyes |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Exceptionally large compared to other eyes within the same taxonomic group | Varies depending on the species, but generally larger than average |
| Shape | Spherical or slightly elongated | Can vary, including spherical, elongated, or even compound eyes |
| Structure | Highly intricate internal structure with specialized cells and tissues | Complexity varies depending on the species and visual requirements |
| Function | Enhances predator detection, improves vision in low-light conditions | Functions can vary, such as improved visual acuity, increased field of view, or enhanced depth perception |
These comparisons highlight the diversity of giant eyes across the animal kingdom, reflecting the unique adaptations that have evolved to meet the specific visual needs of different species.
Physiological Adaptations
The lt-f12 giant eye is supported by a range of physiological adaptations that enhance its function, protection, and overall health.
One key adaptation is the presence of specialized muscles that control the movement of the eyelid. These muscles allow for rapid and precise eyelid closure, providing effective protection against external threats.
Additionally, the lacrimal system is highly developed, producing a continuous supply of tears that lubricate and nourish the eye. The tears also contain antimicrobial substances that help to prevent infections.
The internal structure of the lt-f12 giant eye is also optimized for efficient vision. Specialized cells within the retina enhance light sensitivity and color perception, while a large optic nerve ensures rapid transmission of visual information to the brain.
Ecological Significance
The lt-f12 giant eye plays a crucial role in the ecological interactions and behaviors of the species that possess it.
The enhanced predator detection capabilities provided by the giant eye enable the organism to avoid potential threats and increase its chances of survival. The wider field of view also aids in foraging, allowing the organism to spot prey from a greater distance.
Furthermore, the giant eye contributes to the organism’s social interactions. The ability to detect subtle changes in eye movements and expressions can facilitate communication and cooperation within groups.
Future Research Directions
Future research on the lt-f12 giant eye holds the potential to further our understanding of its function, evolution, and ecological significance.
One promising area of investigation is the study of the molecular and genetic mechanisms underlying the development and maintenance of the giant eye. This research could shed light on the evolutionary processes that have shaped this remarkable adaptation.
Additionally, comparative studies with other species that possess giant eyes could provide valuable insights into the diversity of visual adaptations across the animal kingdom. Such comparisons can help us understand the ecological pressures and environmental factors that have driven the evolution of giant eyes.
User Queries
What are the key features of the lt-f12 giant eye?
The lt-f12 giant eye is distinguished by its exceptional size, intricate structure, and specialized eyelid and lacrimal system.
How does the eyelid protect the giant eye?
The eyelid acts as a protective barrier, shielding the giant eye from physical damage, dust, and other environmental hazards.
What is the role of the lacrimal system in the giant eye?
The lacrimal system produces and drains tears, which lubricate the eye, remove foreign particles, and protect against infection.