Money and the federal reserve mastery test – The Federal Reserve’s mastery over money has a profound impact on the U.S. economy. This comprehensive guide explores the Federal Reserve’s role in monetary policy, its tools and mechanisms, and the challenges and opportunities it faces in shaping the financial landscape.
Delving into the intricacies of monetary policy, this guide provides a detailed examination of the Federal Reserve’s impact on inflation, economic growth, and employment. Empirical evidence supports the analysis, highlighting the potential risks and benefits of different monetary policy approaches.
1. Money and the Federal Reserve
An Overview
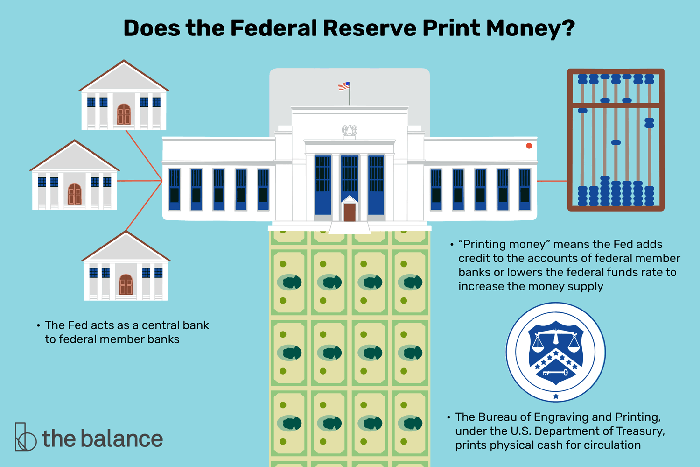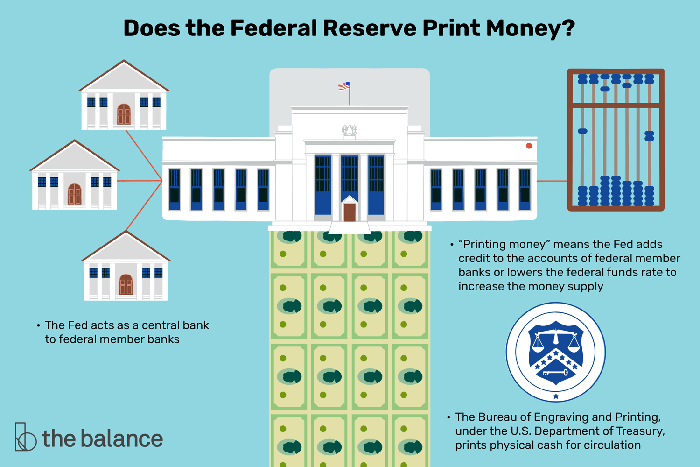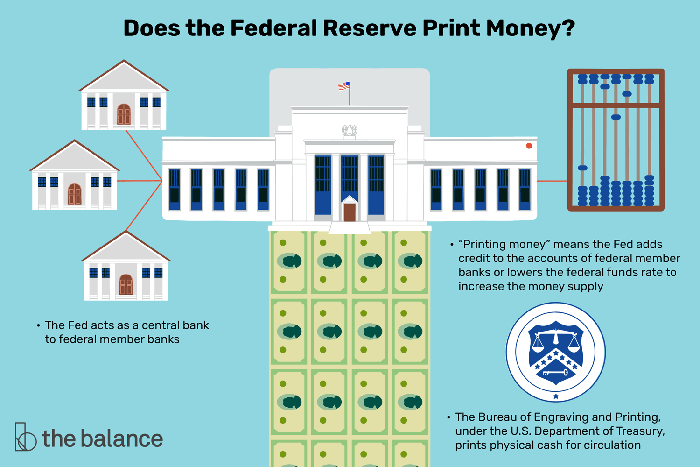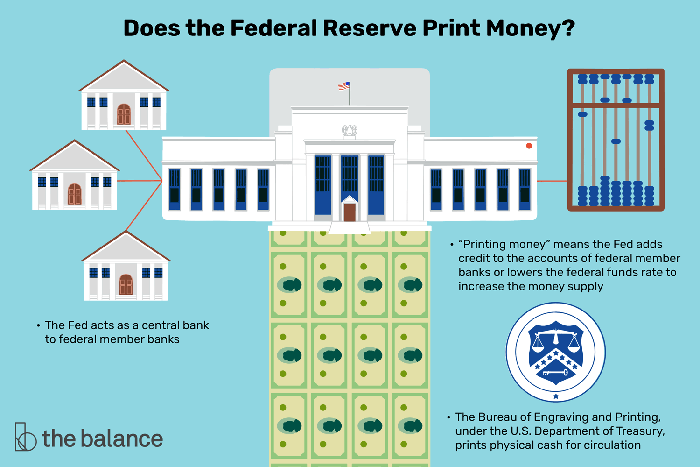
Money plays a crucial role in facilitating transactions, storing value, and serving as a unit of account within an economy. The Federal Reserve (Fed) is the central bank of the United States and holds significant responsibility for managing the monetary system and ensuring its stability.
The Fed’s establishment in 1913 marked a turning point in the evolution of the U.S. monetary system. Prior to its creation, the country faced financial instability and periodic crises due to an uncoordinated banking system and a lack of a central authority to regulate the money supply.
1.1. The Functions of Money
- Medium of exchange: Facilitates the exchange of goods and services.
- Store of value: Holds purchasing power over time.
- Unit of account: Provides a common basis for measuring and comparing the value of different goods and services.
1.2. The Role of the Federal Reserve
- Monetary policy: Sets interest rates and controls the money supply to influence economic activity.
- Bank supervision and regulation: Ensures the safety and soundness of the financial system.
- Financial stability: Promotes stability and resilience in the financial markets.
- Payments system: Oversees the functioning of the nation’s payment systems.
2. Monetary Policy Tools
The Fed utilizes various monetary policy tools to influence economic activity. These tools include:
2.1. Open Market Operations
Buying and selling government securities in the open market to increase or decrease the money supply, respectively.
2.2. Discount Rate
The interest rate charged to banks that borrow from the Fed’s discount window, influencing the cost of borrowing for banks and their customers.
2.3. Reserve Requirements
The amount of reserves that banks are required to hold, which can influence the money supply and the availability of credit.
2.4. Forward Guidance
Public statements by the Fed about its future policy intentions, which can influence market expectations and economic behavior.
3. The Impact of Monetary Policy

Monetary policy has significant effects on the economy, including:
3.1. Inflation
Expansionary monetary policy (lower interest rates, increased money supply) tends to increase inflation, while contractionary policy (higher interest rates, decreased money supply) tends to reduce inflation.
3.2. Economic Growth
Expansionary monetary policy can stimulate economic growth by lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply, while contractionary policy can slow growth by raising interest rates and decreasing the money supply.
3.3. Employment
Monetary policy can influence employment by affecting economic growth and inflation. Generally, expansionary policy tends to increase employment, while contractionary policy tends to decrease employment.
4. Current Monetary Policy Issues
The Fed faces several challenges in managing monetary policy, including:
4.1. Low Inflation
Persistent low inflation makes it difficult for the Fed to raise interest rates without risking deflation.
4.2. Financial Stability Concerns
Loose monetary policy can contribute to asset price bubbles and financial instability.
4.3. Global Economic Conditions
The Fed must consider the impact of global economic conditions on the U.S. economy.
5. The Federal Reserve and Financial Stability
The Fed plays a critical role in maintaining financial stability through:
5.1. Stress Testing
Assessing the resilience of financial institutions to economic shocks.
5.2. Capital Requirements
Setting minimum capital levels for banks to ensure their ability to withstand losses.
5.3. Supervision and Regulation
Monitoring and regulating financial institutions to prevent excessive risk-taking.
6. The Future of Monetary Policy: Money And The Federal Reserve Mastery Test
Monetary policy is likely to evolve in the coming years, driven by factors such as:
6.1. Technological Advancements, Money and the federal reserve mastery test
Fintech and other technological advancements may impact the way monetary policy is conducted.
6.2. Globalization
Increased global interconnectedness may require more coordination among central banks.
6.3. Climate Change
Monetary policy may need to address the economic implications of climate change.
Query Resolution
What is the primary function of the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve is responsible for conducting monetary policy in the United States, aiming to maintain price stability, promote maximum employment, and foster moderate long-term interest rates.
How does the Federal Reserve influence interest rates?
The Federal Reserve uses monetary policy tools, such as open market operations, to influence the supply of money and credit in the economy, which in turn affects interest rates.
What are the potential risks of expansionary monetary policy?
Expansionary monetary policy can lead to inflation, asset bubbles, and financial instability if not managed carefully.