Push and pull factors apush definition provide a foundational understanding of the compelling forces that shape human migration. Push factors, acting as repelling magnets, drive individuals to abandon their homelands, while pull factors, akin to alluring beacons, beckon them towards new destinations.
This interplay of forces orchestrates the complex symphony of human movement.
Throughout history, push and pull factors have played a pivotal role in shaping the ebb and flow of migration. From the Irish Potato Famine to the Syrian Civil War, these factors have propelled countless individuals to embark on arduous journeys in search of refuge, opportunity, or a better life.
Definition of Push and Pull Factors
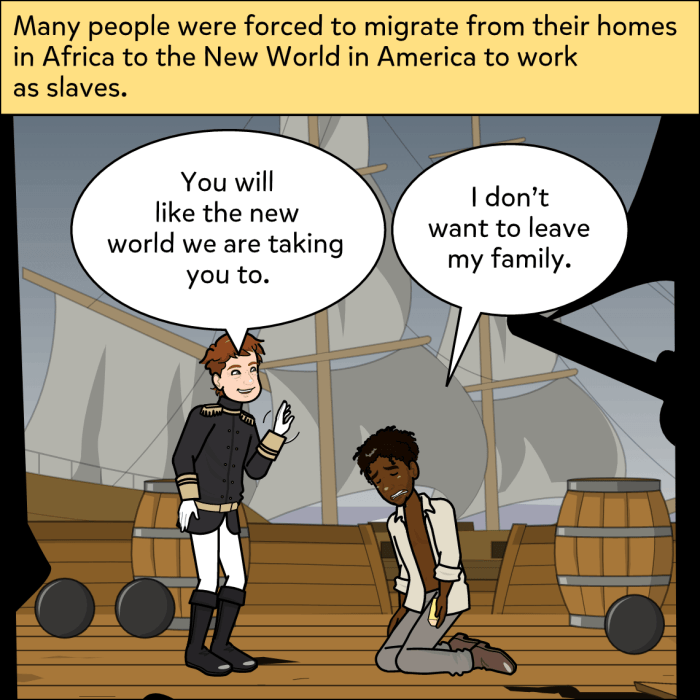
In the context of human migration, push and pull factors are forces that motivate individuals to leave their homelands and relocate to new destinations. Push factors create unfavorable conditions that drive people away, while pull factors offer attractive opportunities that draw them towards specific locations.
Push factors include factors such as war, persecution, poverty, environmental disasters, and political instability. These factors create a sense of insecurity, danger, or lack of opportunity, compelling individuals to seek refuge or better prospects elsewhere.
Pull factors, on the other hand, include factors such as economic opportunities, political freedom, educational opportunities, and a higher standard of living. These factors create a sense of hope, opportunity, and a better future, attracting individuals to migrate towards destinations where they perceive these benefits.
Historical Examples of Push and Pull Factors
Throughout history, push and pull factors have played a significant role in shaping human migration patterns.
| Event | Push Factors | Pull Factors | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| European Immigration to the Americas (16th-19th centuries) | Religious persecution, economic hardship, political oppression | Availability of land, economic opportunities, religious freedom | Mass migration of Europeans to North and South America, transforming the demographics and cultures of these regions |
| Irish Potato Famine (1845-1852) | Crop failure, poverty, disease | Economic opportunities in North America, Australia | Mass migration of Irish people, primarily to the United States, leading to a significant demographic shift |
| World War II (1939-1945) | War, persecution, displacement | Post-war economic recovery, political stability, refugee resettlement programs | Mass migration of refugees and displaced persons to various countries, including the United States, Canada, and Australia |
Modern Examples of Push and Pull Factors

In the contemporary world, push and pull factors continue to drive migration patterns.
- Push factors:Conflict and violence in regions such as Syria, Afghanistan, and Ukraine; economic crises in countries like Venezuela and Zimbabwe; climate change and environmental disasters.
- Pull factors:Economic opportunities in countries like the United States, Canada, and Germany; political stability and democratic freedoms in Western Europe; educational opportunities in the United Kingdom and Australia; higher standards of living in developed countries.
These factors have led to significant migration flows, particularly from developing countries to developed countries, as well as from conflict-ridden regions to neighboring countries and beyond.
Factors Influencing the Strength of Push and Pull Factors
The strength of push and pull factors can vary depending on several factors:
- Personal circumstances:Age, education, skills, financial resources, and family ties can influence an individual’s ability and willingness to migrate.
- Government policies:Immigration laws, refugee resettlement programs, and economic development initiatives can affect the attractiveness of a destination and the ease of migration.
- Economic conditions:Unemployment rates, wages, and cost of living in both the origin and destination countries can influence migration decisions.
Balancing Push and Pull Factors in Migration Decisions
Individuals making migration decisions often weigh the risks and benefits associated with leaving their homelands and moving to new destinations.
- They consider the push factors that are driving them to leave, such as economic hardship or political instability.
- They also consider the pull factors that are attracting them to specific destinations, such as economic opportunities or a higher standard of living.
The decision to migrate is often complex, involving a careful assessment of both push and pull factors and the individual’s personal circumstances and aspirations.
Query Resolution: Push And Pull Factors Apush Definition
What is the primary distinction between push and pull factors?
Push factors originate within an individual’s home country and compel them to leave, while pull factors stem from the destination country and entice them to relocate.
Can push and pull factors coexist within the same migration decision?
Yes, individuals may be simultaneously influenced by both push and pull factors, creating a complex interplay that shapes their migration choices.
How do personal circumstances influence the impact of push and pull factors?
Personal circumstances, such as age, education level, and family ties, can significantly affect how individuals perceive and respond to push and pull factors.