Embarking on an exploration of the Anatomy of the Constitution Answer Key, we delve into a profound understanding of the foundational document that has shaped the United States for over two centuries. This key provides a comprehensive guide to the structure, purpose, and interpretation of the Constitution, offering a deeper appreciation for its enduring legacy and relevance.
Through an in-depth analysis of its key concepts, structure, amendments, historical context, and contemporary applications, we uncover the intricate workings of this vital document, illuminating its enduring impact on American society and jurisprudence.
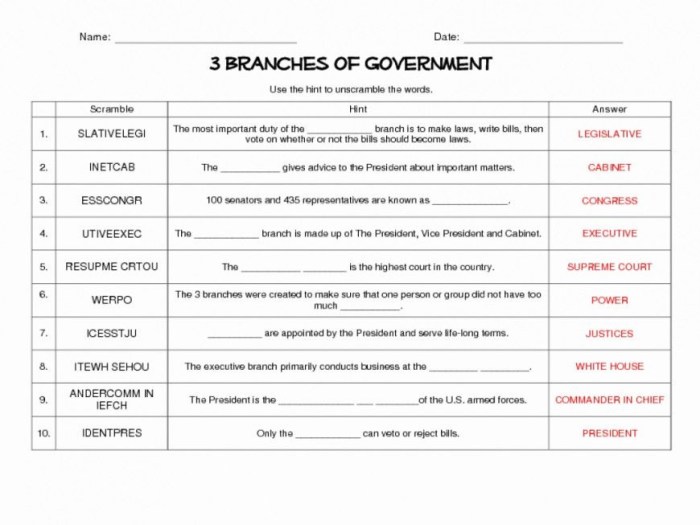
Anatomy of the Constitution: Anatomy Of The Constitution Answer Key
The Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. It defines the framework of the federal government and establishes the basic rights of citizens. The Constitution is divided into three parts: the Preamble, the Articles, and the Amendments.
Key Concepts
Define the anatomy of the constitution
The anatomy of the Constitution refers to the structure and organization of the document. It includes the Preamble, Articles, and Amendments, each of which serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall framework of the Constitution.
Explain the purpose and significance of each part of the constitution
The Preamble sets forth the goals and principles of the Constitution. The Articles establish the structure and powers of the federal government, including the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The Amendments provide for the protection of individual rights and have been added to the Constitution over time to address changing societal needs.
Structure of the Constitution
Provide an overview of the structure of the constitution
The Constitution is organized into seven Articles, each of which addresses a different aspect of the government. The Articles are further divided into sections and clauses, which provide specific details and instructions.
Discuss the different sections and articles of the constitution
Article I establishes the legislative branch, including the powers of Congress. Article II establishes the executive branch, including the powers of the President. Article III establishes the judicial branch, including the powers of the Supreme Court. Articles IV-VII address issues such as the relationship between the states and the federal government, the amendment process, and the ratification of the Constitution.
Amendments to the Constitution
Explain the process for amending the constitution
The Constitution can be amended through a process that involves a two-thirds vote of both houses of Congress and ratification by three-fourths of the states.
Provide examples of significant amendments to the constitution
Significant amendments to the Constitution include the Bill of Rights (Amendments 1-10), which protects individual rights such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly. Other important amendments include the 13th Amendment (abolishing slavery), the 14th Amendment (guaranteeing equal protection under the law), and the 19th Amendment (granting women the right to vote).
Historical Context, Anatomy of the constitution answer key
Discuss the historical context in which the constitution was created
The Constitution was created in 1787 at the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia. The delegates to the convention were motivated by a desire to create a stronger and more effective government than the one that had been established under the Articles of Confederation.
Explain the motivations and influences behind the creation of the constitution
The motivations behind the creation of the Constitution included the need for a more efficient and effective government, the desire to protect individual rights, and the fear of tyranny. The Constitution was also influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment philosophers, such as John Locke and Montesquieu.
Interpretation of the Constitution
Explain the different methods of interpreting the constitution
The Constitution has been interpreted in different ways throughout history. Some of the most common methods of interpretation include originalism, textualism, and living constitutionalism.
Discuss the role of the Supreme Court in interpreting the constitution
The Supreme Court has the power to interpret the Constitution and its decisions are binding on all other courts in the United States. The Court’s interpretations of the Constitution have a significant impact on the way that the Constitution is applied and enforced.
Contemporary Issues
Discuss contemporary issues related to the constitution
The Constitution continues to be a subject of debate and controversy in contemporary society. Some of the most pressing issues related to the Constitution include the role of the government in protecting individual rights, the balance of power between the different branches of government, and the role of the Supreme Court in interpreting the Constitution.
Explain how the constitution is being applied to current events
The Constitution is being applied to current events in a variety of ways. For example, the Supreme Court has recently ruled on cases involving the right to same-sex marriage, the right to bear arms, and the right to religious freedom.
The Constitution is also being used to address issues such as immigration, healthcare, and climate change.
FAQ Insights
What is the purpose of the Anatomy of the Constitution Answer Key?
The Anatomy of the Constitution Answer Key provides a comprehensive guide to the structure, purpose, and interpretation of the United States Constitution, enhancing understanding of its key concepts and historical significance.
How does the Constitution’s structure contribute to its effectiveness?
The Constitution’s structure, with its division into articles and sections, ensures clarity and organization, facilitating its comprehension and implementation.
What is the significance of the amendment process in the Constitution?
The amendment process allows for the Constitution to adapt to changing societal needs and values, ensuring its continued relevance and responsiveness to the evolving landscape.
